The M:E ratio is sensitive to hematologic factors that may impair red blood cell life span, inhibit overall production, or cause dramatic increases in a particular cell line. Each of these conditions reflects bone marrow dynamics through alterations of the M:E ratio. Many observations in the peripheral smear can be traced back to the pathophysiologic events at the level of bone marrow. A perfect example of this is the response of the bone marrow to anemia. As anemia develops and becomes more severe, the patient becomes symptomatic, and the kidney senses hypoxia secondary to a decreased hemoglobin level. Tissue hypoxia stimulates an increased release of erythropoietin (EPO), a red blood cell-stimulating hormone, from the kidney. EPO travels through the circulation and binds with a receptor on the youngest of bone marrow precursor cells, the pronormoblast. Bone marrow has the capacity to expand production 6-8 times in response to an anemic event. Consequently, the bone marrow delivers reticulocytes and nucleated red blood cells to the peripheral circulation prematurely if the kidney senses hypoxic stress. What is observed in the peripheral blood smear is polychromasia (stress reticulocytes, large polychromatophilic red blood cells) and nucleated red blood cells. Both of these cell types indicate that the bone marrow is regenerating in response to an event, a dynamic that represents the harmony between bone marrow and peripheral circulation.
Showing posts with label Hematopoiesis. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Hematopoiesis. Show all posts
Friday, December 11, 2015
Bone Marrow & Myeloid:Erythroid Ratio
The bone marrow is one of the largest organs of the body, encompassing 3% to 6% of body weight and weighing 1500 g in an adult. It is hard to conceptualize the bone marrow as an organ because it is not a solid organ that one can touch, measure, or weigh easily. Because bone marrow tissue is spread throughout the body, one can visualize it only in that context. It is
composed of yellow marrow, red marrow, and an intricate supply of nutrients and blood vessels. Within this structure are erythroid cells (red blood cells), myeloid cells (white blood cells), and megakaryocytes (platelets) in various stages of maturation, along with osteoclasts, stroma, and fatty tissue. Mature cells enter the peripheral circulation via the bone marrow sinuses, a central structure lined with endothelial cells that provide passage for mature cells from extravascular sites to the circulation. The cause and effect of hematologic disease are usually rooted in the bone marrow, the central factory for production of all adult hematopoietic cells. In the first 18 years of life, bone marrow is spread throughout all of the major bones of the skeleton, especially the long bones. As the body develops, the marrow is gradually replaced by fat until the prime locations for bone marrow in an adult become the iliac crest (located in the pelvic area) and the sternum (located in the chest area).
In terms of cellularity, there is a unique ratio in the bone marrow termed the myeloid:erythroid (M:E) ratio. This numerical designation provides an approximation of the myeloid elements in the marrow and their precursor cells and the erythroid elements in the marrow and their precursor cells. The normal ratio of 3:1 to 4:1 reflects the relationship between production and life span of the various cell types. White blood cells have a much shorter life span than red blood cells (6 to 10 hours for neutrophils as opposed to 120 days for erythrocytes) and must be produced at a much higher rate for normal hematopoiesis.
composed of yellow marrow, red marrow, and an intricate supply of nutrients and blood vessels. Within this structure are erythroid cells (red blood cells), myeloid cells (white blood cells), and megakaryocytes (platelets) in various stages of maturation, along with osteoclasts, stroma, and fatty tissue. Mature cells enter the peripheral circulation via the bone marrow sinuses, a central structure lined with endothelial cells that provide passage for mature cells from extravascular sites to the circulation. The cause and effect of hematologic disease are usually rooted in the bone marrow, the central factory for production of all adult hematopoietic cells. In the first 18 years of life, bone marrow is spread throughout all of the major bones of the skeleton, especially the long bones. As the body develops, the marrow is gradually replaced by fat until the prime locations for bone marrow in an adult become the iliac crest (located in the pelvic area) and the sternum (located in the chest area).
In terms of cellularity, there is a unique ratio in the bone marrow termed the myeloid:erythroid (M:E) ratio. This numerical designation provides an approximation of the myeloid elements in the marrow and their precursor cells and the erythroid elements in the marrow and their precursor cells. The normal ratio of 3:1 to 4:1 reflects the relationship between production and life span of the various cell types. White blood cells have a much shorter life span than red blood cells (6 to 10 hours for neutrophils as opposed to 120 days for erythrocytes) and must be produced at a much higher rate for normal hematopoiesis.
Saturday, November 28, 2015
Thymus
The thymus is a lymphopoietic organ located in the upper part of the anterior mediastinum. It is a bilobular organ demarcated into an outer cortex and central medulla. The cortex is densely packed with small lymphocytes (thymocytes), cortical epithelial cells, and a few macrophages. The medulla is less cellular and contains more mature thymocytes mixed with medullary epithelial cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. The primary purpose of the thymus is to serve as a compartment for maturation of T lymphocytes. Precursor T cells leave the bone marrow and enter the thymus through arterioles in the cortex. As they travel through the cortex and the medulla, they interact with epithelial cells and dendritic cells, which provide signals to ensure that T cells can recognize foreign antigen but not self-antigen. They also undergo rapid proliferation. Only about 3% of the cells generated in the thymus exit the medulla as mature T cells. The rest die by apoptosis and are removed by thymic macrophages. The thymus is responsible for supplying the T-dependent areas of lymph nodes, spleen, and other peripheral lymphoid tissue with immunocompetent T lymphocytes.
The thymus is a well-developed organ at birth and continues to increase in size until puberty. After puberty, however, it begins to atrophy until in old age it becomes barely recognizable. This atrophy could be driven by increased steroid levels beginning in puberty and decreased growth factor levels in adults. The atrophied thymus is still capable of producing new T cells if the peripheral pool becomes depleted as occurs after the lymphoid irradiation that accompanies bone marrow transplantation.
FIGURE: A schematic drawing of the thymus. Hassall’s corpuscles are collections of epithelial cells that may be involved in the development of certain (regulatory) T cell subsets in the thymus.
Extramedullary Hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis in the bone marrow is called medullary hematopoiesis or intramedullary hematopoiesis.
Blood cell production in hematopoietic tissue other than bone marrow is called extramedullary hematopoiesis.
In certain hematologic disorders when hyperplasia of the marrow cannot meet the physiologic blood needs of the tissues, extramedullary hematopoiesis can occur in the hematopoietic organs that were active in the fetus, principally the liver and spleen. Organomegaly frequently accompanies significant hematopoietic activity at these sites. This extramedullary hematopoiesis in postnatal life reflects the ability of inert hematopoietic cells to become active, functional cells if the need arises.
Thursday, November 26, 2015
Sites of Hematopoiesis
Sites of Hematopoiesis
Yolk sac
From the 18th day after fertilization, the yolk sac begins hematopoiesis. The cells made here are erythrocytes & few macrophages.
Aorta-gonads-mesonephros (AGM) region
Located along the developing aorta. This region has the ability to make a wider range of hematopoietic cells including lymphocytes.
At about the 3rd
month of fetal life, the yolk sac & AGM discontinue their role in hematopoiesis.
Liver
At about the 3rd
month of fetal life, the liver becomes the chief site of blood cell production. The liver continues to produce a high proportion of erythroid cells, but myeloid and lymphoid cells begin to appear in greater numbers.
As fetal development progresses, hematopoiesis also begins to a lesser degree in the spleen, kidney, thymus, and lymph nodes. Erythroid and myeloid cell production as well as early B cell (lymphocyte) development gradually shifts from these sites to bone marrow during late fetal and neonatal life as the hollow cavities within the bones begin to form.
Bone Marrow
The bone marrow becomes the primary site of hematopoiesis at about the 6th
month of gestation and continues as the primary source of blood production after birth and throughout adult life.
The thymus becomes the major site of T cell (lymphocyte) production during fetal development and continues to be active throughout the neonatal period and childhood until puberty.
Lymph nodes and spleen continue as an important site of late B cell differentiation throughout life.
NOTE
Liver & spleen may return to hematopoiesis after birth if necessary in a process called extramedullary hematopoiesis (production of blood cells outside the bone marrow).
Thursday, November 19, 2015
Functions of the Spleen
Hematopoietic function:-
- Can produce white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets if necessary.
Reservoir function:-
- One-third of platelets and granulocytes are stored in the spleen.
Filtration functions:-
- Aging red blood cells are destroyed.
- Spleen removes inclusion from red blood cells.
- If red blood cell membrane is less deformable or antibodycoated, spleen presents a hostile environment leading to production of spherocytes.
Immunologic function:-
- Opsonizing antibodies are produced, trapping and processing antigens from encapsulated organs.
Saturday, November 7, 2015
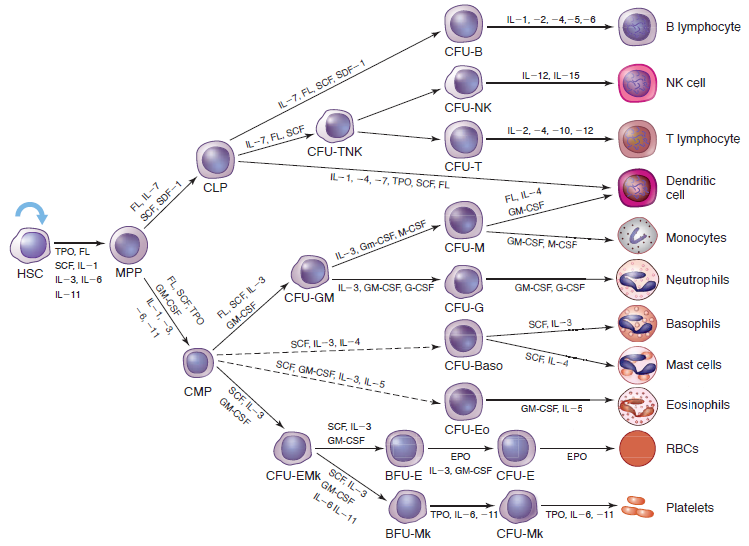
Lineage-specific Cytokine Regulation
LINEAGE-SPECIFIC CYTOKINE REGULATION
Erythropoiesis:
In the erythroid lineage, progenitor cells give rise to two distinct types of erythroid colonies in culture. A primitive progenitor cell, the BFU-E, is relatively insensitive to EPO and forms large colonies after 14 days in the form of bursts. Production of BFU-E colonies was originally described as being supported by burst-promoting activity, or BPA, now known to be IL-3 or GM-CSF. CFU-E colonies grow to maximal size in 7 to 8 days and depend primarily on EPO. The CFU-E are the descendants of BFU-E and subsequently give rise to the first recognizable erythrocyte precursor, the pronormoblast. Other cytokines reported to influence production of red cells include IL-9, IL-11, and SCF. However, EPO is the pivotal humoral factor that functions to prevent apoptosis and induce proliferation/differentiation of the most committed erythroid progenitor cells and their progeny.
Granulopoiesis and Monopoiesis:
Granulocytes and monocytes are derived from a common bipotential progenitor cell, the CFU-GM, derived from CFUGEMM. Specific GFs for granulocytes and monocytes, acting synergistically with GM-CSF and/or IL-3, support the differentiation pathway of each lineage. M-CSF supports monocyte differentiation while G-CSF induces neutrophilic granulocyte differentiation. Eosinophils and basophils also are derived from the CFU-GEMM under the influence of growth factors IL-5 and IL-3/IL-4, respectively.
Megakaryocytopoiesis/Thrombopoiesis:
Platelets are derived from megakaryocytes, which are progeny of the CFU-EMk. CFU-Mk are induced to proliferate and differentiate into megakaryocytes by several cytokines. However, the cytokines that induce the greatest increase in platelet production are IL-11 and TPO.
Lymphopoiesis:
The growth and development of lymphoid cells from the common lymphoid progenitor cell occurs in multiple anatomic locations including the bone marrow, thymus, lymph nodes, and spleen. Multiple GFs play a role in T and B lymphocyte growth and development, most of which act synergistically.
Friday, November 6, 2015
Cytokines and the Control of Hematopoiesis
Hematopoietic growth factor cytokines are specific glycoproteins that regulate and control hematopoiesis.
Functions of hematopoietic growth factor cytokines:-
Functions of hematopoietic growth factor cytokines:-
- Promote cell survival (suppress apoptosis).
- Promote proliferation.
- Control & regulate the processes of differentiation.
Characteristics of Growth Factors:-
- Produced by stromal cells in B.M. (except: Epo).
- Generally, more than one GP needed to control hematopoietic.
- React with specific membrane receptors.
- Affect hematopoiesis directly or indirectly.
- Act synergistically with each other.
- The majority have multiple biologic activities (not lineage specific).
- GP = Glycoprotein.
Early-Acting (Multilineage) GFs
- Act on multipotential precursor cells.
- SCF, FL, IL-3, GM-CSF, IL-6 & IL-11 .
SCF:
- SCF = Stem Cell Factor = Steel Factor “SF” = kit ligand “KL” = Mast Cell Growth Factor “MCGF” .
- Proliferation & differentiation of CFU-GEMM, CFU-GM, CFU-Mk, BFU-E.
- Also promotes the survival, proliferation & differentiation of mast cell precursors.
- Plays role in normal melanocyte development & gametogenesis.
Flt3 ligand (FL):
- Increases recruitment of primitive HSC into the cell cycle & inhibits apoptosis.
- Flt3 ligand has little effect on unilieage BFU-E/CFU-E, CFU-mast cell or CFU-Eo but it is a potent stimulator of granulocytic, B cell, & dendritic cell proliferation & differentiation.
- HSC = Hematopoietic Stem Cell.
IL-3:
- Affects multilineage progenitor cells & early commited progenitors like BFU-E.
- Also has indirect actions & can can induce the expression of other cytokines.
GM-CSF:
- Affects CFU-GEMM, BFU-E, CFU-Mk, CFU-GM, & CFU-Eo.
- GM-CSF: it is a major promoter of granulocyte & monocyte differentiation, but lacks a significant effect on basophil production.
- GM-CSF also activates the functional activities of most nature phagocytes, including neutrophils, macrophages & eosinophils.
IL-6 & IL-11:
- They are pleiotropic cytokines with overlapping growth stimulatory effects on myeloid & lymphoid cells as well as on primitive multilineage cells.
- Significant effects on megakaryopoiesis & platelet production.
- Both also mediate the acute phase response of hepatocytes. Also they are major pyrogens in vivo.
IL-11:
- Shortens the duration of G0 of primitive hematopoietic progenitor cell & hastens hematopoietic recovery after treatment with cytotoxic agents or B.M. transplantation.
Later-Acting (Lineage-Restricted) GFs
- G-CSF : granulocytes.
- M-CSF : monocytes. (Also regulates the genesis of osteoclasts).
- EPO : RBCs.
- TPO : megakaryocytes & platelets.
- IL-5 : eosinophils. (Also stimulates lymphocyte development).
- The other interleukins important in lymphopoiesis (ILs-2, -4, -7, -10, -12, -13, -14, -15).
Erythropoietin (EPO):
- The only cytokine to function as true hormone.
- Embryonic life: produced largely by liver.
- Adult life: largely produced by kidney (~ 90%), & by liver (to a lesser extent; ~ 10%).
- Production is regulated by the oxygen needs; induced by hypoxia.
- Stimulates growth, survival, & differentiation of erythroid progenitor cells (major effect on CFU-E); & stimulates proliferation & RNA synthesis in more well-differentiated maturing cells.
- Reticulocytes & mature erythrocytes do not have receptors for EPO; so they are not affected by EPO.
Thrombopoietin (TPO):
- TPO = mpl-ligand = megakaryocyte growth & development factor (MGDF). Megakaryocyte & platelet production.
- In vitro, make/primes mature platelets to respond to aggregation-inducing stimuli & increases the platelet release reaction.
- Act with a variety of other GFs (SCF, IL-3, FL) to stimulate the growth of primitive progenitor cell.
Indirect-Acting Growth Factors
- Some cytokines that regulate hematopoiesis do so indirectly.
- Example: IL-1 .
- IL-1: has no colony-stimulating activity itself, but it induces neutrophilic leukocytosis, resulting from the release of other direct-acting cytokines by accessory cells.