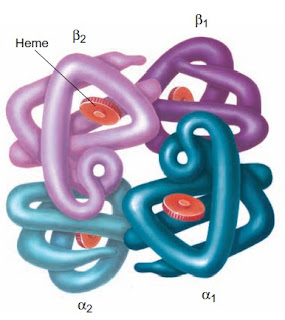
HbA1C on chromatography is a minor component of normal adult hemoglobin (HbA) that has been modified posttranslationally (HbA3 on starch block electrophoresis). A component usually has been added to the N terminus of the β-chain. The most important subgroup of HbA1 is HbA1C , which has glucose irreversibly attached. This hemoglobin is referred to as glycosylated hemoglobin. HbA1C is produced throughout the erythrocyte’s life, its synthesis dependent on the concentration of blood glucose. Older erythrocytes typically contain more HbA1C than younger erythrocytes having been exposed to plasma glucose for a longer period of time. However, if young cells are exposed to extremely high concentrations of glucose ( >400 mg/dL) for several hours, the concentration of HbA1C increases with both concentration and time of exposure.
Measurement of is routinely used as an indicator of control of blood glucose levels in diabetics because it is proportional to the average blood glucose level over the previous two to three months.
Measurement of is routinely used as an indicator of control of blood glucose levels in diabetics because it is proportional to the average blood glucose level over the previous two to three months.
Average levels of HbA1C are 7.5% in diabetics and 3.5% in normal individuals.














0 comments:
Post a Comment