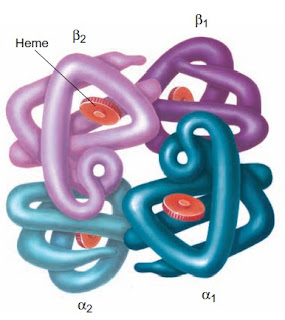
The Role of 2,3-Diphophoglycerate
The major function of the hemoglobin molecule is the transport of oxygen to the tissues. The oxygen affinity of the hemoglobin molecule is associated with the spatial rearrangement of the molecule and is regulated by the concentration of phosphates, particularly 2,3-DPG in the erythrocyte. The manner in which 2,3-DPG binding to reduced hemoglobin (deoxyhemoglobin) affects oxygen affinity is complex. Basically, 2,3-DPG combines with the beta chains of deoxyhemoglobin and diminishes the molecule’s affinity for oxygen.
When the individual heme groups unload oxygen in the tissues, the beta chains are pulled apart. This permits the entrance of 2,3-DPG and the establishment of salt bridges between the individual chains. These activities result in a progressively lower affinity of the molecule for oxygen. With oxygen uptake in the lungs, the salt bonds are sequentially broken; the beta chains are pulled together, expelling 2,3-DPG; and the affinity of the hemoglobin molecule for oxygen progressively increases.
In cases of tissue hypoxia, oxygen moves from hemoglobin into the tissues, and the amount of deoxyhemoglobin in the erythrocytes increases. This produces the binding of more 2,3-DPG, which further reduces the oxygen affinity of the hemoglobin molecule. If hypoxia persists, depletion of free 2,3-DPG leads to increased production of more 2,3-DPG and a persistently lowered affinity of the hemoglobin molecule for oxygen.
Figure: Hemoglobin molecular changes